Football, or soccer as it is known in some regions, is a sport cherished and celebrated worldwide.
With its mesmerizing display of skill, teamwork, and strategy, football has captured the hearts of millions.
One of the fascinating aspects of this beautiful game lies in the diverse roles and positions each player assumes on the field.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the various positions in football, exploring the unique responsibilities and contributions of each player.
Different Positions in Football
1. Goalkeeper
The guardian of the net, the goalkeeper is the last line of defense. Their primary objective is to prevent the opposing team from scoring goals.
A goalkeeper must possess quick reflexes, exceptional agility, and fearless bravery to dive into a crowd of players to make crucial saves.
Their ability to communicate effectively with the defenders is paramount, as they serve as the eyes and voice from the backline.
Check out all the goalkeeper rules and detailed guide here.
2. Defenders
Defenders are responsible for safeguarding their team’s goal and preventing the opponents from advancing into dangerous scoring areas.
This position can be further broken down into several roles:
a. Center-backs: Positioned at the heart of the defense, center-backs are tall, strong, and adept at winning aerial duels. They act as the primary barrier against opposing strikers and are pivotal in organizing the defensive line.
b. Full-backs: Operating on the flanks of the defense, full-backs have a crucial dual role. They need to defend against wingers and opposing attackers while also supporting the team’s attacks by delivering crosses into the box.
3. Midfielders
Often referred to as the engine room of the team, midfielders are versatile players who dominate the central area of the pitch. Their responsibilities vary depending on their specific role:
a. Defensive Midfielders (Holding Midfielders): Positioned just in front of the defense, they focus on intercepting passes, breaking up opposition attacks, and distributing the ball efficiently to initiate attacks for their team.
b. Central Midfielders (Box-to-Box Midfielders): These players cover large distances during a match, contributing both defensively and offensively. They link the defense with the attack, making key passes, and occasionally scoring goals.
c. Attacking Midfielders (Playmakers): Operating behind the strikers, these creative players are responsible for unlocking the opposing defense with precise passes, vision, and intelligent movement.
4. Wingers
Wingers are positioned on the flanks of the pitch, close to the touchline. They are also basically midfielders.
Their primary objective is to use their pace, dribbling skills, and crossing ability to create goal-scoring opportunities for the forwards.
They often cut inside to shoot or pass and can be game-changers with their individual brilliance.
5. Forwards (Strikers)
The goal poachers, the forwards, are the players responsible for scoring goals.
They need to possess a lethal combination of goal-scoring instinct, positioning, and composure in front of the net.
Strikers are often the most celebrated players, as they are the ones who find the back of the net and secure victory for their team.
Some Important FAQs related to Positions in Football:
1. What are the exact names of each position in Football?
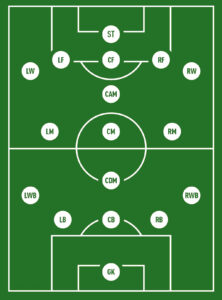
There are 17 different positions on a football field. Often players play on one or more of these positions. They are:
- Goal Keeper (GK)
- Center Back (CB)
- Right Back (RB)
- Left Back (LB)
- Left Wing Back (LWB)
- Right Wing Back (RWB)
- Central Defensive Midfielder (CDM)
- Central Midfielder (CM)
- Left Midfielder (LM)
- Right Midfielder (RM)
- Central Attacking Midfielder (CAM)
- Left Winger (LW)
- Right Winger (RW)
- Center Forward (CF)
- Left Forward (LF)
- Right Forward (RF)
- Striker (ST)
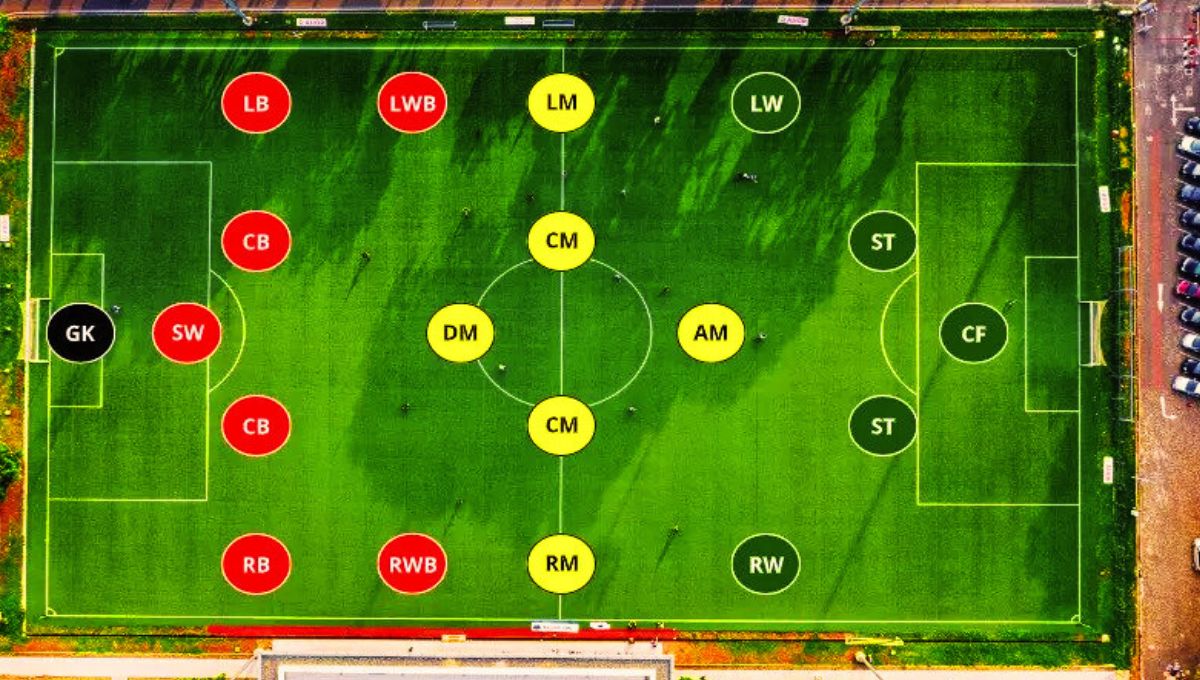
Below is an image providing the names of each position on a football field:
Breakdown of each position:
Goalkeeper (GK)
Goalkeeper is a player positioned in front of the goal whose main responsibility is to prevent the opposing team from scoring by stopping shots on target.
There is no variation in the goalkeeper position. They all have a “GK” sign.
But based on the style some keepers are sweeper keepers like Manuel Neuer who sometimes come out to play, but that’s only possible when your team gets lots of position and is literally the bully in the league.
Defenders
- Right-back (RB): The defender who plays on the right side of the defensive line.
- Left-back (LB): The defender who plays on the left side of the defensive line.
- Center-back (CB): The defenders who play in the central part of the defensive line.
Midfielders
- Defensive Midfielder (CDM): The midfielder primarily responsible for defensive duties and protecting the backline.
- Central Midfielder (CM): The midfielder who operates in the center of the field and contributes both defensively and offensively.
- Left Midfielder (LM): This midfielder is positioned on the left side of the central midfield and closer to the left touchline. Their role involves a mix of offensive and defensive responsibilities. They are expected to support the left-back in defensive duties while also contributing to the team’s attacking play. Left midfielders often use their pace and skill to deliver crosses into the opponent’s penalty area and create goal-scoring opportunities for the forwards.
- Right Midfielder (RM): This midfielder plays a similar role but on the right side of the central midfield and closer to the right touchline. Like their counterpart on the left, right midfielders are expected to balance defensive support and attacking contributions. They use their speed and dribbling ability to beat opponents and deliver accurate crosses or passes to set up goal-scoring opportunities.
- Attacking Midfielder (CAM): The midfielder who focuses on creating goal-scoring opportunities for the forwards plus scoring goals themselves when the opportunity arrives.
Forwards
- Right Winger (RW): The forward positioned on the right side of the attacking line.
- Left Winger (LW): The forward positioned on the left side of the attacking line.
- Center Forward/Striker (CF/ST): The forward positioned in the central part of the attacking line, whose main task is to score goals.
2. What is number 8 position in football?
In football, the number 8 position refers to the Central Midfielder (CM) who wears the jersey number 8. The number 8 position is typically associated with a dynamic and versatile midfielder who operates in the central areas of the field.
Central midfielders (number 8) play a crucial role in both defensive and offensive phases of the game.
They are often responsible for linking the defense with the attack, controlling the tempo of the game, and distributing the ball to other players.
A number 8 midfielder is expected to have a well-rounded skill set, including good passing ability, vision, ball control, and tactical intelligence.
Some key attributes of a number 8 midfielder include:
- Passing Skills: They should be able to deliver accurate short and long passes to teammates and initiate attacks from the midfield.
- Work Rate: Number 8 midfielders are known for their high work rate and endurance, as they need to cover a lot of ground during a match.
- Defensive Awareness: They are required to contribute defensively by making tackles, interceptions, and pressing the opposition.
- Goal-Scoring Threat: Number 8 midfielders often have the ability to score goals from midfield and make late runs into the opponent’s box.
Famous Number 8s in Football:
Famous footballers who have excelled in the number 8 position in the past include Steven Gerrard, Frank Lampard, and Andres Iniesta.
In the current era, the best number 8s are Toni Kroos, Martin Ødegaard, and Pedri.
The position remains a vital part of various football formations and is highly valued for its all-around contributions to the team.
3. What’s a false 9? or a number 9 role in football
A “False 9” and a “Number 9” refer to two distinct roles in football, both associated with the striker position, but with different styles of play.
False 9:
The False 9 is a tactical variation of the traditional striker role.
In this position, the player deployed as the striker operates in a deeper and more withdrawn position than a typical center forward (Number 9).
Instead of playing as a fixed and central striker, the False 9 drops deeper into the midfield, often between the lines of the opposition’s defense and midfield.
The primary objective of the False 9 is to create confusion in the opposing defense by dragging center-backs out of position and pulling the defense apart.
This movement creates spaces for the wingers or attacking midfielders to exploit.
The False 9 is also adept at linking play, acting as a playmaker, and distributing the ball to teammates in advanced positions.
Famous False 9 Players:
Famous footballers who have excelled as False 9s include Lionel Messi during his time at Barcelona and Francesco Totti during certain periods of his career at AS Roma.
Isco also played this role very well under Carlo Ancelotti for Real Madrid.
In current times, Kevin De Bruyne plays the role of false 9 under Guardiola sometimes and he probably is the best for this role among all the players in the world.
Number 9:
The Number 9, often simply referred to as the striker or center forward, is the traditional and more classic role of a forward player.
The Number 9 typically operates as the furthest forward player in the team, positioned centrally in the attacking line.
Their primary goal is to score goals and be the main focal point of the team’s attacking play.
Number 9s are usually strong, tall, and skilled at holding up the ball with their back to the goal, allowing their teammates to join the attack.
They are excellent finishers and thrive on receiving crosses, through balls, or other goal-scoring opportunities inside the penalty area.
Famous number 9s:
Famous Number 9s in football history include players like Ronaldo Nazario, Gabriel Batistuta, and Robert Lewandowski, known for their goal-scoring prowess and ability to lead the attacking line.
Which one is better? False 9 or number 9?
They are both good. Both roles, the False 9 and the traditional Number 9, can be highly effective in different tactical setups, and coaches choose the role that best suits their team’s style of play and the players available to them.
Managers can’t force a role in the team if players are not available for it, and if they did it will be a tactical blunder.
4. What’s number 10 role in football?
The “Number 10” role in football is a prestigious and iconic position traditionally associated with attacking midfielders who wear the jersey number 10.
The Number 10 is often referred to as the “playmaker” or “attacking midfielder” and is considered the creative hub of the team’s attack.
The primary responsibilities of a Number 10 include:
- Creativity: The Number 10 is the chief playmaker on the team. They are highly skilled at creating goal-scoring opportunities for their teammates through precise passing, vision, and creativity.
- Vision: Number 10s have an exceptional ability to read the game and spot openings in the opposition’s defense. They can deliver through balls, long passes, and set pieces to unlock defenses.
- Dribbling: These players are usually gifted dribblers, capable of taking on defenders and creating space for themselves and others.
- Goal Scoring: While their primary role is to create chances for others, Number 10s are also expected to contribute with goals. They can shoot accurately from distance and find themselves in scoring positions during attacks.
- Link-Up Play: The Number 10 acts as a crucial link between the midfield and the forward line, connecting the team’s build-up play and attacking phases.
Famous number 10s:
Historically, some of the greatest footballers in history have played as Number 10s, and the position holds a special place in football lore.
Famous examples include Diego Maradona, Pele, Michel Platini, Zinedine Zidane, and more recently, Lionel Messi.
Role of number 10 nowadays:
In modern football, the role of the Number 10 has evolved, and different tactical systems may use variations of the attacking midfielder position.
Some teams may deploy a more classic central attacking midfielder, while others may use “inverted wingers” or “false 10s” who operate from wider positions but still fulfill the creative responsibilities of the traditional Number 10.
Regardless of the specific tactical approach, the Number 10 role remains vital for teams looking to control and dictate the flow of the game in the attacking third of the field.
Before you go…
Check out our article on 17 basic rules of football. It will help you understand the game even further. 🙂